
- #Checkmate 9la publication trial#
- #Checkmate 9la publication plus#
- #Checkmate 9la publication series#
Conclusion: With 2 years’ minimum follow-up, first-line NIVO + IPI + chemo demonstrated durable survival and benefit versus chemo in pts with advanced NSCLC no new safety signals were identified. Any grade and grade 3–4 treatment-related adverse events were reported in 92% and 48% of pts in the NIVO + IPI + chemo arm vs 88% and 38% in the chemo arm, respectively. Similar clinical benefit with NIVO + IPI + chemo vs chemo was observed in all randomized pts and across the majority of subgroups, including by PD-L1 expression level (Table) or histology.
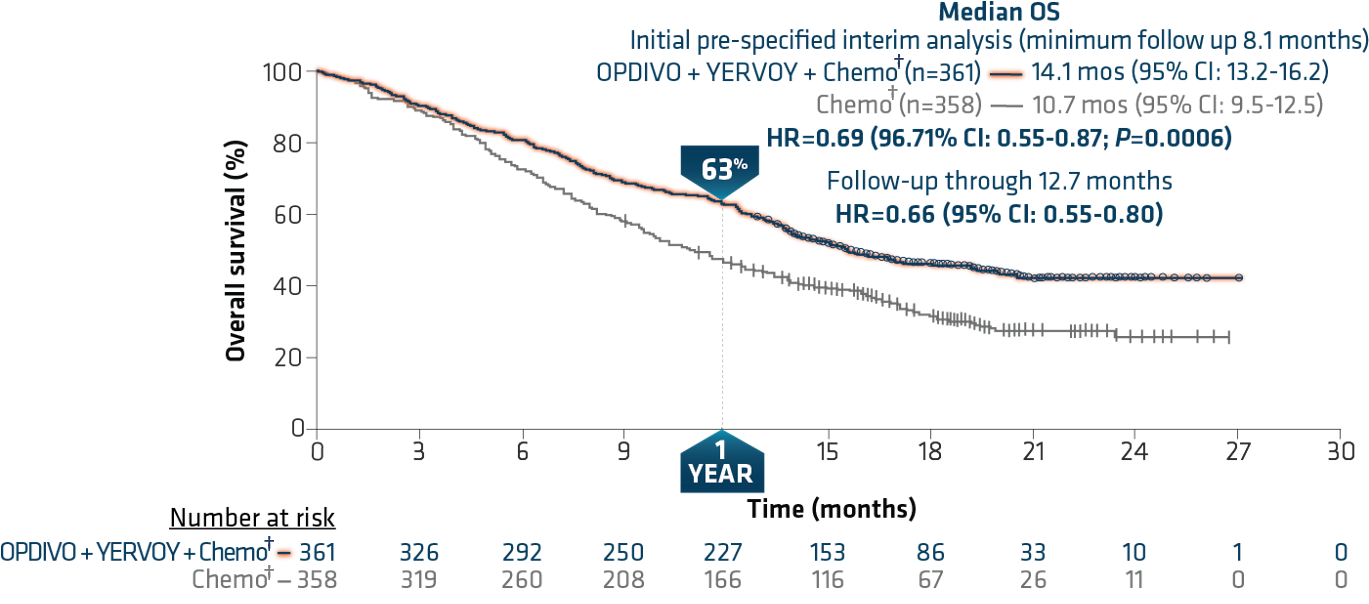
ORR was 38% with NIVO + IPI + chemo vs 25% with chemo. Median PFS with NIVO + IPI + chemo vs chemo was 6.7 months vs 5.3 months (HR, 0.67 ) 8% and 37% of pts who had disease progression received subsequent immunotherapy, respectively. Results: At a minimum follow-up of 24.4 months for OS (database lock: Feb 18, 2021), pts treated with NIVO + IPI + chemo continued to derive OS benefit vs chemo, with a median OS of 15.8 months vs 11.0 months, respectively (HR, 0.72 ) 2-year OS rates were 38% vs 26%. Secondary endpoints included PFS and ORR by blinded independent central review, and efficacy by different PD-L1 levels. Pts with non-squamous NSCLC in the chemo-alone arm could receive pemetrexed maintenance. Methods: Adult patients (pts) with stage IV / recurrent NSCLC, ECOG performance status ≤ 1, and no known sensitizing EGFR/ALK alterations were stratified by PD-L1 (< 1% vs ≥ 1%), sex, and histology (squamous vs non-squamous) and were randomized 1:1 to NIVO 360 mg Q3W + IPI 1 mg/kg Q6W + chemo (2 cycles n = 361) or chemo alone (4 cycles n = 358). Here we report data with 2 years’ minimum follow-up from this study. Clinical benefit was observed regardless of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression level and histology.
#Checkmate 9la publication trial#
In the randomized phase 3 CheckMate 9LA trial (NCT03215706), first-line NIVO + IPI combined with 2 cycles of chemo significantly improved overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and objective response rate (ORR) vs chemo alone (4 cycles).

Universidad Complutense de Madrid = Complutense University of Madrid īristol Myers Squibb Thérapies Laser Assistées par l'Image pour l'Oncologie - U 1189 Oncology Institute of Bucharest Professor Doctor Alexandru Trestioreanu Hospital Universitari i Politècnic La Fe = University and Polytechnic Hospital La Fe Immunogenic Cell Death and Mesothelioma Therapy SF Nectarie Oncology Center Īmbulatorium Chemioterapii The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Healthcare Ltd., part of Springer Nature.Institutul oncologic Prof Dr Ion Chiricuta NIC was unlikely to be cost-effective as a first-line treatment for patients with advanced NSCLC.Ĭost-effectiveness Markov model Nivolumab Non-small cell lung cancer. The results of one-way sensitivity analysis showed that the hazard ratio of overall survival was the most sensitive parameter. The INHB was - 0.28 QALY, and the INMB was - $41,865 at the threshold of $150,000/QALY.
#Checkmate 9la publication plus#
Our results showed that NIC versus chemotherapy alone cost $264,278 and yielded an additional 0.80 quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), which led to an ICER of $202,275/QALY gained. CheckMate 9LA (NCT03215706), a phase 3, randomized, open-label study in first-line advanced NSCLC, showed significantly improved overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and objective response rate (ORR) with nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with 2 cycles of chemotherapy versus 4 cycles of chemotherapy alone, with a manageable.
#Checkmate 9la publication series#
A series of sensitivity analyses were performed to analyze the uncertainty of the model. Model outputs included the incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs), incremental monetary benefit (INMB), and incremental net-health benefit (INHB). Cost and utility were obtained from the literature. The clinical data were derived from the CheckMate 9LA trial. We aimed to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of NIC for advanced NSCLC from the US payer perspective.Ī Markov model has been established to predict the disease course of previously untreated advanced NSCLC. The effectiveness of nivolumab plus ipilimumab with two cycles of chemotherapy (NIC) for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been demonstrated.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
